Names and short parametres of processors. A part 2.
Evgenie Rudometov, Victor Rudometov.
authors@rudometov.com
Article is grounded on substances of books "Arrangement of the multimedia computer" and "Motherboards and chip sets"
For three ten years of intensive perfection of processors the large quantity of these extremely important units which differ as solid-state technology, by the architecture and konstruktivom, and the price, and functionality, including productivity has been released. Not only new, but also many of early models are successfully maintained as a part of the computers which are now for users. Thus quite often in the technical literature and instructions use not only firm trading names of processors, but internal names of these products and their architectures that complicates identification of products.
To attempt of classification of names of processors and their architectures with coercion of key parametres the substances presented more low are resulted.
(A part 2, Intel: from P5 to Pentium II/III)
From time of release by the corporation of Intel of the first-ever processor has transited hardly more than three tens years. For this time the given corporation inspecting, by the way, already more of 80 % of the market of processors, it has been released hundred millions these extremely important units. Thus they had different architectures, types and names. Some data of the released products of Intel will be resulted further.
The note
Despite a high-scale of reliability of used sources, in the resulted data separate inaccuracies can contain.
Processors of the corporation of Intel, released in the seventieth and eightieth years
|
CPU |
The clock |
Digit capacity |
K-in transistors, |
The addressed |
The virtual |
|
i4004 |
0,108 |
4 |
2 300 |
640 byte |
- |
|
i8008 |
0,108 |
8 |
3 500 |
16 Kbytes |
- |
|
i8080 |
2 |
8 |
6 000 |
64 Kbytes |
- |
|
i8086 |
5, 8, 10 |
16 |
29 000 |
1 Mb |
- |
|
i8088 |
5, 8 |
8 |
29 000 |
1 Mb |
- |
|
i80286 |
6-12,5 |
16 |
134 000 |
16 Mb |
1 Gbyte |
|
i386DX |
16-33 |
32 |
275 000 |
4 Gbytes |
64 Tbyte |
|
i386SX |
16-33 |
16 |
275 000 |
4 Gbytes |
64 Tbyte |
|
i486DX |
25-50 |
32 |
1 200 000 |
4 Gbytes |
64 Tbyte |
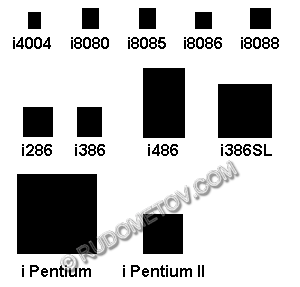
Fig. 1. Dimensions in matching

Fig. 2. IBM PC of the sample 1981года with the processor of Intel 8088
Generation processors i486, created on the basis of a front line on that time processing technique possessed rather high parametres. However, despite it, the new, more powerful processors of P5 architecture received the name of Pentium and possessing higher clock rates, have step-by-step superseded the predecessors. Though, it is necessary to recognise, processors i486 were released rather long time in a parallel way from Pentium. Moreover, the processor i486DX4 (i80486DX4) has been released already after issue of the first representatives of the following generation presented by models of Pentium of 60 MHz and Pentium of 66 MHz.
Pentium (60, 66 MHz) — on March, 22nd, 1993 Working clock rates 60, 66 MHz. The processor with frequency of 60 MHz (frequency of the bus of 60 MHz) provided 100 million operations a second (70.4 SPECint92, 55.1 SPECfp92 on system Xpress from 256 Kbytes of the cache memory of the second level), 66 MHz (frequency of the bus of 66 MHz) — 112 million op/with (77.9 SPECint92, 63.6 SPECfp92 on system Xpress from 256 Kbytes of the cache memory of the second level), 3,1 million transistors, processing technique BiKMOP (BiCMOS) 0,8 microns, the external data bus of 64 bits, the bus of 32 address of bats, internal digit capacity of 32 bits, the addressed memory of 4 Gbytes, the virtual storage of 64 Tbyte, power supply 5 V.Chislo of contact electrodes 273 (a pug-in package — PGA). Dimensions of 5,49 unit sm h 5,49 see Are intended for desktop PCs.

Fig. 3. A kernel of the processor of Intel of Pentium
Pentium (75 MHz) — on October, 10th, 1994 Working clock rate of 75 MHz, frequency of the bus of 50 MHz, 126,5 million op/with (2.31 SPECint95, 2.02 SPECfp95 on system Gateway from 256 Kbytes of the cache memory of the second level), 3,2 million transistors, processing technique BiKMOP 0,6 microns, the external data bus of 64 bits, the bus of 32 address of bats, internal digit capacity of 32 bits, the addressed memory of 4 Gbytes, the virtual storage of 64 Tbyte, power supply 3,3 V.Chislo of contact electrodes 320 (tank on a film carrier — TCP, 2,4 h 2,4 sm), 296 (tank with the pin grid array, allocated in chessboard order — SPGA, 5 sm h 5 sm). Are intended for notebooks and desktop PCs.
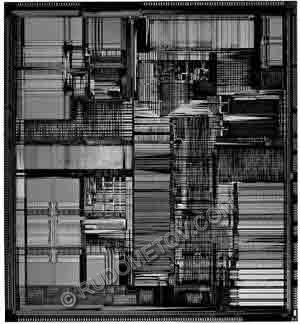
Fig. 4. A kernel of the processor of Intel of Pentium
Pentium (90, 100 MHz) — on March, 7th, 1994 Working clock rates 90, 100 MHz. The processor with frequency of 90 MHz (frequency of the bus of 60 MHz) provided 149,8 million op/with (2.74 SPECint95, 2.39 SPECfp95 on system Gateway from 256 Kbytes of the cache memory of the second level), 100 MHz (frequencies of the bus of 50 and 66 MHz) — 166,3 million op/with (3.30 SPECint95, 2.59 SPECfp95 on system Gateway from 256 Kbytes of the cache memory of the second level), 3,2 million transistors, processing technique BiKMOP 0,6 microns, the external data bus of 64 bits, the bus of 32 address of bats, internal digit capacity of 32 bits, the addressed memory of 4 Gbytes, the virtual storage of 64 Tbyte, power supply 3,3 V.Chislo of contact electrodes 296 (a pug-in package — PGA, 5 sm h 5 sm). Are intended for desktop PCs.
Pentium (120 MHz) — on March, 27th, 1995 Working clock rate of 120 MHz (frequency of the bus of 60 MHz), 203 million op/with (2.72 SPECint95, 2.81 SPECfp95 on system Xxpress from 1 Mb of the cache memory of the second level), 3,2 million transistors, processing technique BiKMOP 0,6 and 0,35 microns, the external data bus of 64 bits, the bus of 32 address of bats, internal digit capacity of 32 bits, the addressed memory of 4 Gbytes, the virtual storage of 64 Tbyte, power supply 3,3 V.Chislo of contact electrodes 296 (PGA, 5 sm h 5 sm). Are intended for notebooks and desktop PCs.
To pass to razrelu Processors
 English
English Russian
Russian German
German