Current technologies in the architecture of motherboards on i440BX
(Continuation)
Evgenie Rudometov, Victor Rudometov.
authors@rudometov.com
Article is grounded on substances of books "Arrangement of the multimedia computer" and "Motherboards and chip sets"
< <К предыдущей странице статьи
By modern criteria an essential lack of a chip set i440BX is absence of support of protocols above UltraDMA/33. In total several years ago the performance level, set by the specified mode was considered as very considerable reaching as provided a transfer rate of the information to 33 Mb per second. But now this metric is considered already insufficient. Operation of modern hard disks demands the new high-speed modes set by UltraDMA/66 protocols (66 Mb per second), UltraDMA/100 (100 Mb per second), hard disks supported by all main manufacturers (IBM, Quantum, Western Digital, Seagate, Fujitsu, Maxtor etc .).
Implementation of the controllers providing new high-speed modes, is carried out in the majority of architectures of new chip sets. However it is frequent this problem manufacturers of motherboards solve installation of the additional controller. So mode UltraDMA/66 is often carried out by means of specialised chips, for example, High Point HPT 366, and UltraDMA/66/100 — High Point HPT 370. By means of such chips the given possibilities in some motherboards of Abit corporation, and also in a number of products of other corporations releasing similar cards are realised.
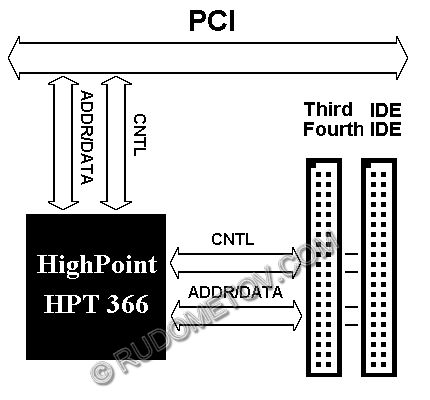
Controller UltraDMA/66 inclusion in the architecture of the computer with a chip set i440BX AGPset
Quite often systems with chip High Point HPT 370 except implementation of modes UltraDMA/66 and UltraDMA/100, provide possibilities of processing technique RAID. Three modes RAID, defining three its levels are Thus accessible. It is necessary to remind, that level RAID (RAID level) defines features of representation and an information storage, in particular, a degree of used redundancy and algorithm of allocation of data between disks in the array of arrangements. In computers
In mode RAID 0 (stripping mode for boosting performance), 2 hard disks demanding not less, are carried out splitting (stripping) files on smaller blocks and rectangular distribution of these blocks between several disks of the array of arrangements. It increases speed of data access and, in particular, reduces loadtime of programs. However the given mode does not increase a degree of data protection in case of glitches, damages of a surface of disks and an output of arrangements out of operation. For this purpose uses RAID 1, providing possibility of protection of the information at its storage, usage and modification.
In mode RAID 1 (mirroring mode for data security), demanding, as well as in case of RAID 0, not less than 2 hard disks, backup — mirroring (mirroring) data is carried out at their storage on hard disks. It provides data protection and some increase in speed at a read operation, however it does not concern the data record, carried out usually more slowly, than at RAID 0. However it managed to be overcome in following mode RAID — RAID 0+1.
In mode RAID 0+1 (stripping and mirroring), known the same as RAID 1/0 and RAID 10, and 4 disk drives demanding usually not less, are carried out also splitting of data (stripping), and their mirroring (mirroring), than provided both increase in speed of data access, and rise of level of their protection and stability to their damage.
To pass to razrelu Motherboards and chip sets
 English
English Russian
Russian German
German